
HELLO, I'M
Luis Wallace
Mathematics Graduate & Data Explorer.
About
MY JOURNEY
Hi, I’m Luis Wallace — a Mathematics graduate exploring the world through data. Here you’ll find projects that uncover patterns, solve problems, and tell stories with numbers.
Each project reflects a different aspect of my journey — from digging into messy datasets and building clear visualisations, to applying statistical tests and crafting thoughtful narratives around the results. I enjoy finding structure in complexity and making data feel intuitive, whether I’m working with code, charts, or written analysis.
Air Quality Trends - Newcastle
Project Overview
Air pollution is a major public health concern. This project investigates air pollution patterns across Newcastle, focusing on how levels of key pollutants — such as nitrogen dioxide (NO₂) and particulate matter (PM2.5 and PM10) have changed over time. Using publicly available environmental data, I analysed daily and seasonal fluctuations, long-term trends, and the impact of external factors, including introduction of a Clean Air Zone (CAZ).
Tools & Techniques
Languages: R
Data Sources: Envitech UK Air Data
Methods: Time series analysis, data cleaning, correlation analysis

Analytical Approach
The study explores:
-
General pollution trends — including seasonal variation, daily patterns, and extremes.
-
Impact assessment — comparing pre- and post-CAZ NO₂ levels to identify any significant changes.
-
Causality — considering whether observed reductions can be attributed to the CAZ or other factors.
Key Insights Summary
-
NO₂ Levels Show Mixed Trends — Preliminary data suggests a modest decline in NO₂ concentrations at monitoring stations within the Clean Air Zone (CAZ) since its implementation in January 2023, with more noticeable reductions after July when exemptions for light goods vehicles ended.
-
Seasonal and Daily Patterns Persist — Pollution levels remain higher during winter months and peak during morning and evening rush hours, consistent with traffic-related emissions.
-
CAZ Impact Is Promising but Not Isolated — While reductions align with the CAZ timeline, other factors like weather, traffic, and post-COVID behavior also play a role. Notably, pollutant levels, which were occasionally hazardous before, have not exceeded safe limits since the CAZ implementation.
-
Policy Comparison with London’s ULEZ — London’s Ultra Low Emission Zone has led to substantial NOx reductions, offering a benchmark for Newcastle’s CAZ.
Limitations
-
Some data sets had missing values or inconsistent formats
-
Weather and socioeconomic factors not fully accounted for
-
Further work could include machine learning for prediction


Spatial Analysis- Squirrel data
Project Overview
This project uses reported grey squirrel sightings from 2020 and 2022 to analyse their spatial distribution and examine how patterns have shifted over time. The findings can inform conservation planning, help assess potential impacts on native species such as the red squirrel, and guide wildlife management strategies. More generally, tracking changes in species distribution over time contributes to biodiversity monitoring, early detection of ecological pressures, and the development of evidence-based environmental policies.

Tools & Techniques
Languages: R
Data Sources: CSV file containing sightings
Methods: Choropleth mapping, rate-of-change analysis, spatial density analysis
Analytical Approach
The study explores:
-
Spatial distribution and its best modes of presentation.
-
Changes in the distribution over time, highlighting areas of expansion.
-
Hotspots of sightings and potential factors influencing their spread.

Key Insights Summary
-
Identified Key Population Hubs — Employed detailed choropleth mapping techniques to effectively visualise population concentrations, highlighting regions where the majority of inhabitants are clustered. This provided a clear, accessible representation of demographic density and spatial distribution.
-
Analysed Regional Population Growth — Conducted a comprehensive examination of long-term demographic trends to pinpoint areas experiencing the most significant population increases. This analysis not only captured the scale of change but also revealed the dynamics of regional growth patterns.
-
Uncovered Geographic Correlations — Demonstrated a compelling relationship between latitude and proportional population growth, revealing that certain latitudinal bands correspond with stronger demographic expansion. This insight adds a critical geographic dimension to understanding population dynamics.
Limitations
-
Reliance on Sightings — Observed sightings may not accurately reflect true spatial distribution, as they depend on human observation and reporting.
-
Short Time Frame — Data covering only two years may not capture short-term fluctuations or longer-term population trends.
-
Regional Sample Variability — Limited sample sizes in certain regions could reduce the reliability of spatial analyses and affect overall conclusions.

Text Analysis- of a Book and Customer Reviews
Project Overview
Sentiment analysis assigns an emotional value to each word—positive, negative, or neutral—and combines these to approximate the overall emotional tone of a sentence, page, or even an entire chapter. Here, I demonstrate its potential by analysing the evolution of emotional intent in a book and in customer reviews from two competitors, using these insights to offer practical recommendations.
Tools & Techniques
Languages: R
Data Sources: 'Frankenstein' the novel (in text doc), CSV files of customer reviews of cookies
Methods: Sentiment Analysis, TF-IDF, Comparative box plots
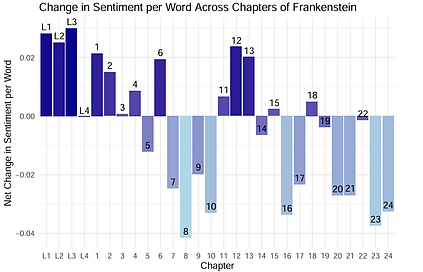
Analytical Approach
This project showcases a data-driven approach to text analysis, including:
-
Tracking emotional trends to understand how sentiment evolves across large text datasets.
-
Analysing word frequency and context-specific vocabulary to uncover patterns and key insights.
-
Comparative sentiment analysis to identify differences in overall and average sentiment across multiple sources.
Key Insights Summary
-
Sentiment dynamics — Clear patterns in emotional tone emerged, with peaks and troughs aligning to specific themes or events in the text, illustrating how the overall tone shifts over time.
-
Vocabulary highlights — Discovered which words were most frequent overall and which were uniquely associated with particular sections, providing insight into context-specific language use.
-
Comparative trends — Revealed measurable differences in sentiment between companies, highlighting areas of strength and weakness.
-
Actionable takeaways — Insights could inform marketing strategies, content optimisation, or audience engagement approaches.

Limitations
-
Context sensitivity: Sentiment analysis can misinterpret sarcasm, irony, or nuanced language, potentially producing misleading scores.
-
Data bias: Results are influenced by the dataset; uneven representation or small sample sizes can skew insights.
-
Domain dependence: I used general sentiment models which may perform less accurately on review texts than more specified models
About Me.
Practicing Power BI
Project Overview
Exploring the capabilities of Power BI by presenting stock data.
Used drill down and refresh functions to create an informative, dynamic dashboard.
Tools & Techniques
Program: Power BI
Data Sources: HSBC daily stock data from June to October
Methods: Data reformatting, drill down, filtering, summarisation

Analytical Approach
The study explores:
-
Drill down capabilities in Power BI
-
The powerful filtering and presentation tools
-
The power query editor and refresh in Power BI
Key Insights Summary
-
User-friendly interface with intuitive drag-and-drop features:
The layout allows new users to build visuals quickly without needing advanced technical skills. Most task, such as connecting to data, creating charts, and designing dashboards, can be done through simple interactions. -
The data engine behind Power BI is highly capable, allowing you to create complex calculations, relationships, and measures.

Limitations
-
The visuals are easy to use but more restrictive than, for example, R

